Class: CSE 120 Subject: computer-science computer-architecture Date: 2025-04-07 Teacher: **Prof. Nath
Transistors
Denard Scaling
- Denard Scaling is a way to scale transistor parameters(including voltage) to keep power density constant
A question to ask is, if transistor size has kept decreasing (250nm in 1997 to 2nm in 2025), why has frequency started flatlining?
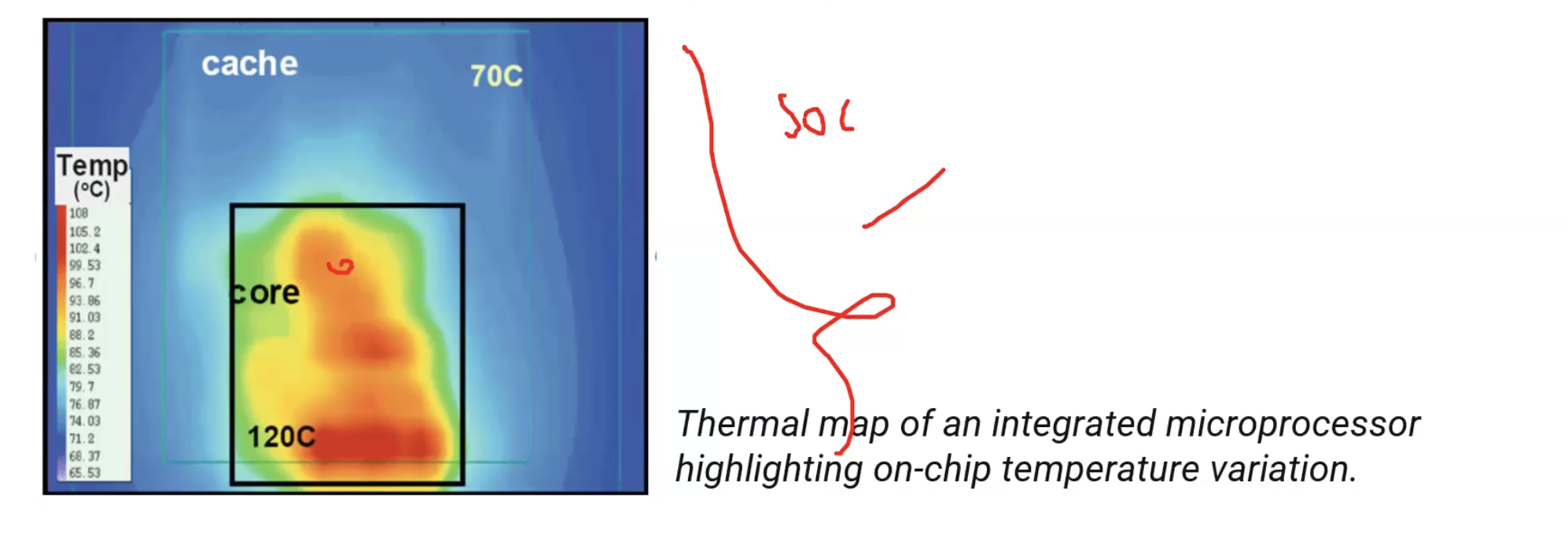
End of Denard Scaling
- a huge drawback to Denard Scaling is that it ignored the “leakage current” and “threshold voltage” which establish a baseline of power per transistor.
- as a result, it has created a “power wall” that has limited processor frequency to around 4GHz since 2006(yikes!)
Potential Improvements
- Using multiple cores
- Parallelism
- Speculative prediction
Performance
Latency
- latency is the interval between stimulation and response(basically how long it takes to do a task)
Base Units
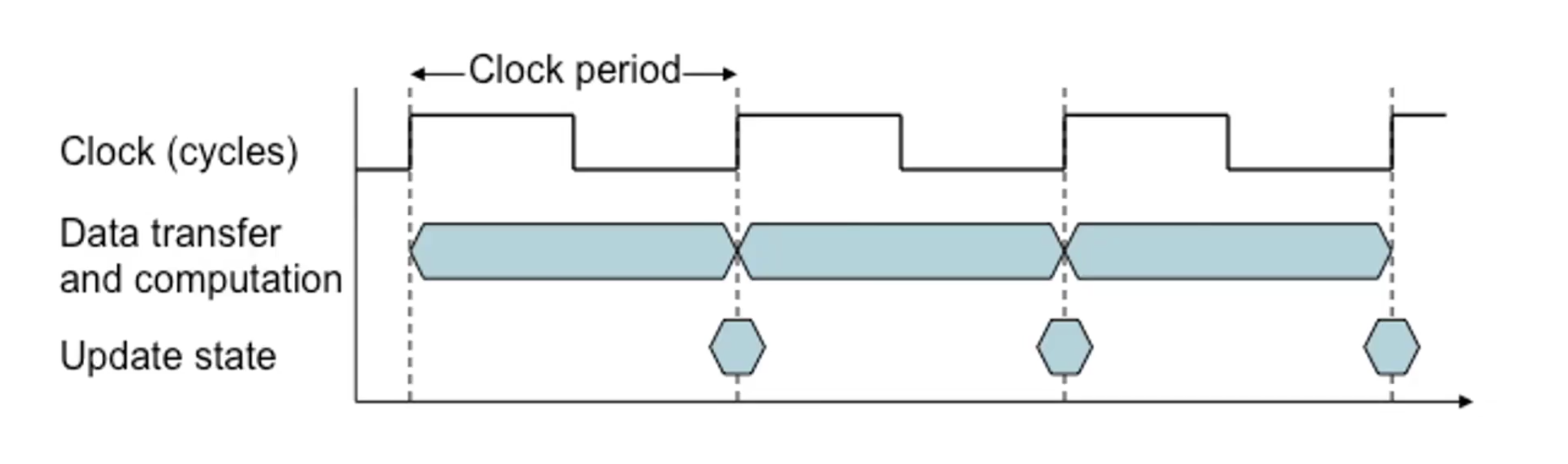
Clock Period
- clock period refers to the duration of a clock cycle
- i.e.
- this is the basic unit of time in all computers
Clock Frequency/Rate/Speed
- clock frequency/clock rate/clock speed is cycles per second
- i.e.
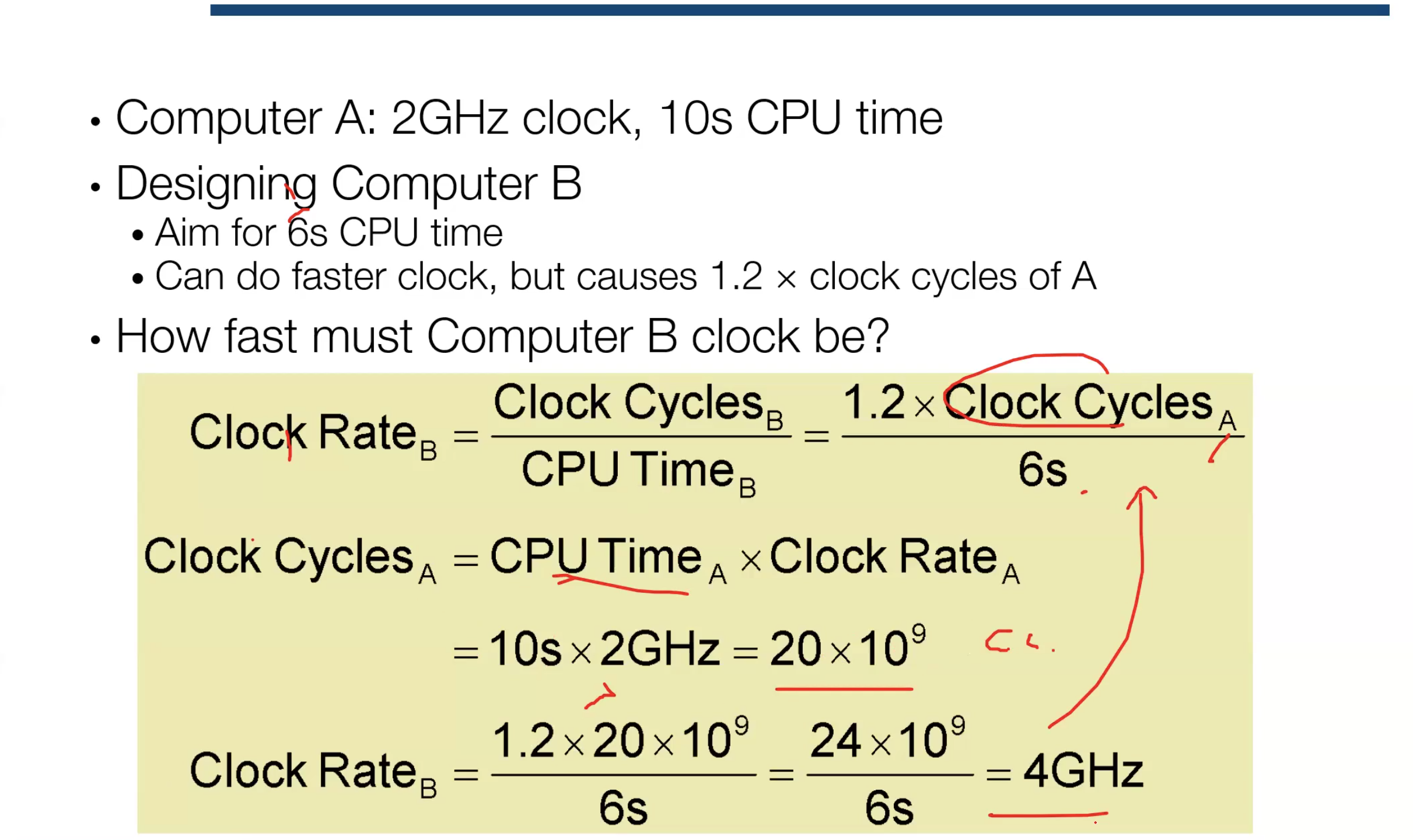
Execution Time
- Execution Time = Cycles Per Program * Clock Cycle Time
- which is also the same as = Cycles Per Program / Clock Frequency/Rate/Speed
Ways to Increase Execution Time
- Reduce the Cycles Per Program
- Increase the Clock Frequency
Bandwidth
- bandwidth is also known as throughput
- bandwidth refers to how much of work is done in a given time.
Speed Up
- performance overall improved execution for a whole problem
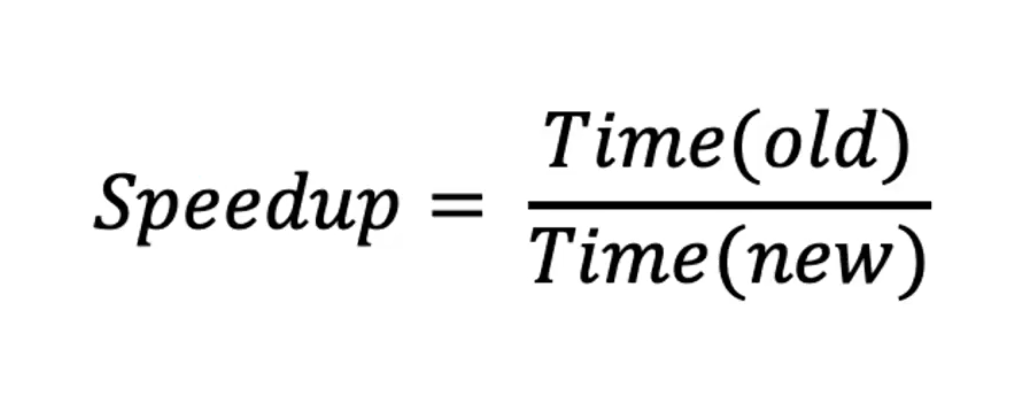
- for future reference, use (times or x)
- i.e. 2.1x speed up
is throughput the inverse of latency? yes if the tasks are done one after the other no if the tasks are done in parallel
Little’s Law
- Little’s Law refers to the average number of transactions in a stable system is equal to their average arrival rate, multiplied by their average time in the system.
Parallelism
- parallelism is equal to throughput(bandwidth) * latency
Amdahl’s Law
- refers to the maximum possible speed up achievable by optimizing a part of a system
- = fraction of time improved
- = how much faster that part gets
Example
- What is the overall speedup if half of the execution sped up by 2x?
= 0.5 = 2