2025-09-22 22:27
Status: adult
Tags: leetcode leetcode-medium dynamic-programming google Leetcode
House Robber
Code
class Solution(object):
def rob(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(nums)
if n == 1:
return nums[0]
if n == 2:
return max(nums[0], nums[1])
prev = nums[0]
cur = max(nums[0], nums[1])
for i in range(2, n):
prev, cur = cur, max(nums[i] + prev, cur)
return curExplanation
- We have 2 base case:
- if the length of the array is 1, just return the only element
- If the length of the array is 2, return the max of the 2 elements
- To understand our next approach, analyze this photo
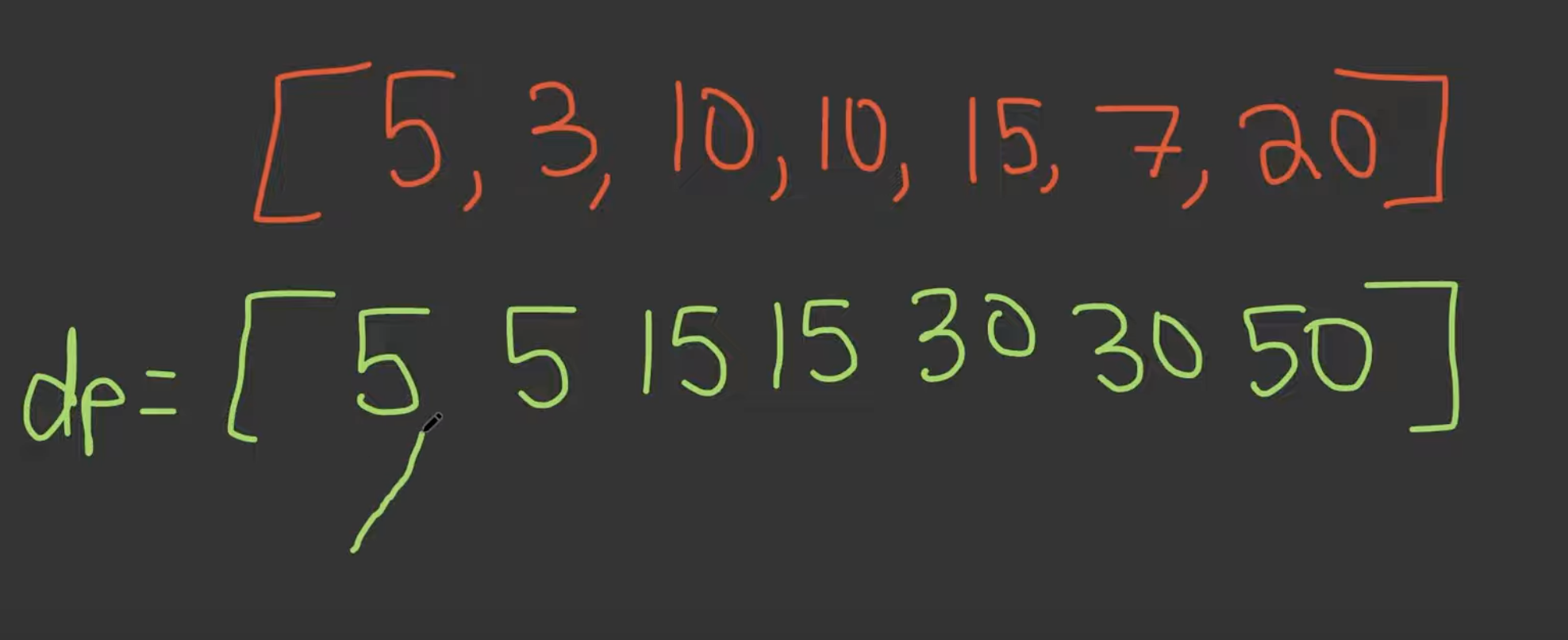
- Let’s look at the 3 index since we have accounted for the edge cases. If we choose to rob 10, we have to also add the money from 2 steps back because we can’t rob adjacent houses = .
- Also we can not rob and just keep the 10. In this case robbing is better because .
- We repeat this until we reach the end
- We can use memoization and have a dp array with the same length as the input array, initialized all to 0’s. i.e. dp = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
- A clever trick to save space is to use a prev and cur variable.
- prev is set to nums[0] and cur = max(nums[0], nums[1]).
- Iterate from 2 to n(length of nums)
- prev = cur and cur = max(nums[i] + prev(which is from 2 steps back), cur)
- return cur